
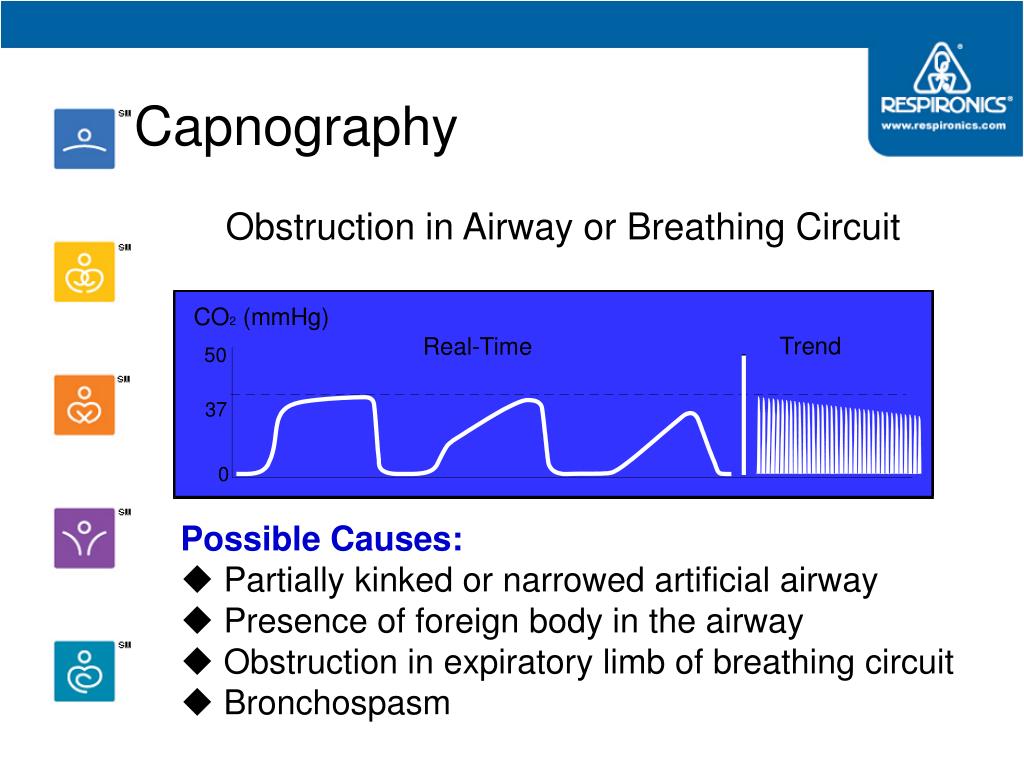
Correlation studies done between the assessment methods and indices readings did not show strong correlations either between the measurements or the magnitude of change pre-treatment and post-treatment. On the capnographic waveform, there was a significant difference in the slope of phase 3 (p < 0.001) and alpha angle (p < 0.001), but not in phase 2 slope (p = 0.35). Peak flow measurements showed significant improvements post-treatment (p < 0.001). A p value of below 0.05 was taken to be significant. Simple and canonical correlations were performed to determine correlations between the assessment methods. The pre-treatment and post-treatment results were then compared with paired samples t-test analysis. After treatment, when they were adjudged well for discharge, a second set of results was obtained for peak flow measurements and capnographic waveform recording. The patients were treated according to departmental protocols.
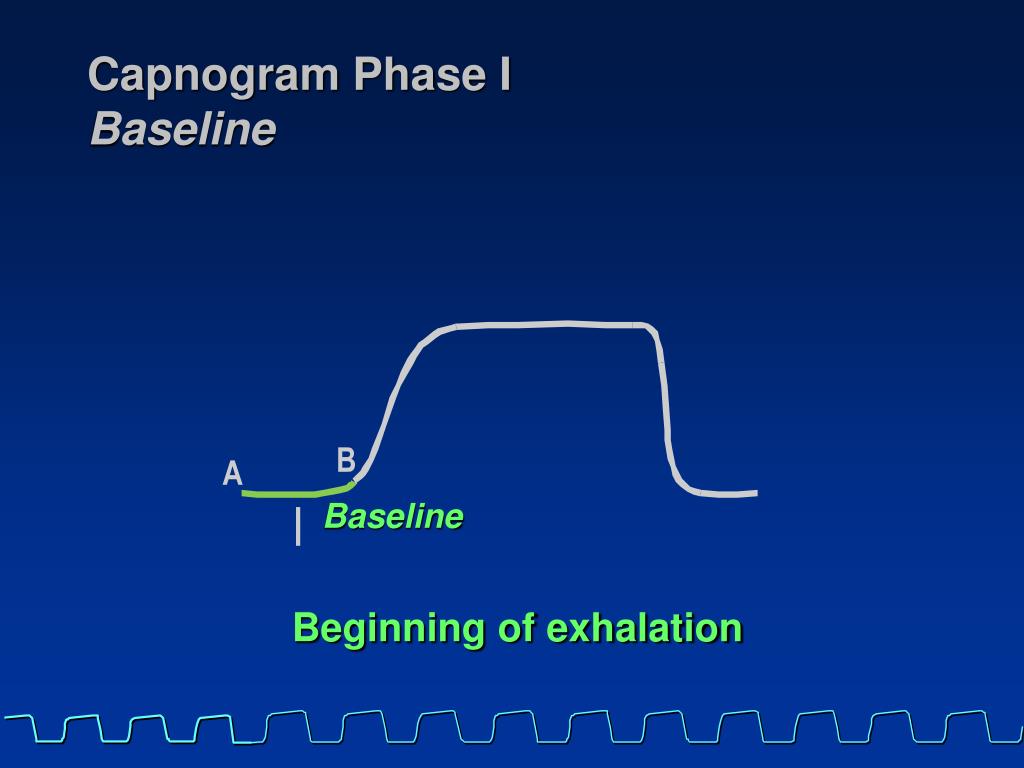
The capnographic waveform was recorded onto a PC card for indices analysis. One hundred and twenty eight patients with acute asthma were monitored with peak flow measurements and then had a nasal cannula attached for microstream sampling of expired carbon dioxide. We carried out a prospective study in a university hospital emergency department (ED). Our objective was to compare and assess the correlation between the changes in capnographic indices and peak flow measurement in non-intubated acute asthmatic patients attending the emergency room. The changes in asthma include decrease in slope of phase 2, increase in slope 3 and opening of angle alpha. The normal capnogram has an almost square wave pattern comprising phase 1, slope phase 2, plateau phase 3, phase 4 and angle alpha (between slopes 2 and 3). We were looking into other methods for the initial asthma assessment, namely the use of capnography. Both methods have their own disadvantages such as poor cooperation/effort from patients (peak flow meter) and lack of objective assessment (clinical parameters). The usual method for initial assessment of an acute asthma attack in the emergency room includes the use of peak flow measurement and clinical parameters.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
